IEEE P2660.1 Recommendation Practices on Industrial Agents: Integration of Software Agents and Low-Level Automation Functions
Paulo Leitao and Thomas Strasser
Background and Motivation
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) is a paradigm derived from the distributed artificial intelligence field that offers an alternative way to design complex large-scale systems by decentralizing the control system by distributed, autonomous and cooperative entities [1]. It mainly differs from conventional approaches due to its inherent capabilities to adapt to emergence without external intervention. The MAS concept is usually pointed out as a suitable approach and technology to distribute intelligence in applications from smart production, smart logistics, smart health, smart cities and smart electrical grids. Industrial agent-based solutions, aligned with the Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) perspective, impose additional requirements namely in terms of flexibility, robustness, scalability and responsiveness to industrial automation systems.
A key challenge in industrial agents is the interface between the intelligent software agent (acting as the cyber part) and the low-level automation device (acting as the physical part), e.g., smart meters, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or robots. Currently, the practices to integrate the software agent with the physical hardware device are not homogeneous and usually developed case-by-case or in a proprietary manner.
Proposed Approach and Solution
In order to achieve full interoperability, a standardized way for the integration of these two layers is necessary to allow reusability and transparency. For this purpose, the IEEE P2660.1 Working Group (WG) is developing activities regarding the definition of recommendation practices on industrial agents focusing the integration of software agents and low-level automation functions. This WG is sponsored by the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IES) and the IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Society (SMC), as well as technically sponsored by the IEEE IES Technical Committee on Industrial Agents, the IEEE IES Technical Committee on Smart Grids, and the IEEE SMC Technical Committee on Intelligent Industrial Systems.
The proposed recommendation aiming to standardize the interface process to achieve reusability and transparency, will support and help engineers to leverage the best practices of developing industrial agents for automation control problems and given application fields, in the emergent context of CPS. Internally, a structure of subs-groups was created to agile the development of activities. Three sub-groups are considered to collect and analyze the existing practices in different application domains, i.e., one for factory automation, another for power and energy systems, and also one for building automation. A testing sub-group is responsible to perform the testing and validation of the identified recommended practices.
The results from an initial survey related to the analysis of the existing practices on interfacing software agents and low-level automation functions, published in [2], shows that Java is mainly used as agent technology (followed by C++) and that interfaces usually use a kind of proprietary protocols, follow a coupled approach and the client/server interaction mode, as well as a focus on read/write operations on the digital I/O interaction. Additionally, usually security is not considered in this kind of interfaces. These results allowed deriving four generic templates for interface practices, classified according to location (i.e., on-device, where the agent and the low-level control are running in the same device, or hybrid where the agent and the low-level control are running in different computational platforms) and mode of interaction (client-server and publish-subscribe schemas) as shown in Fig. 1 [3]. .
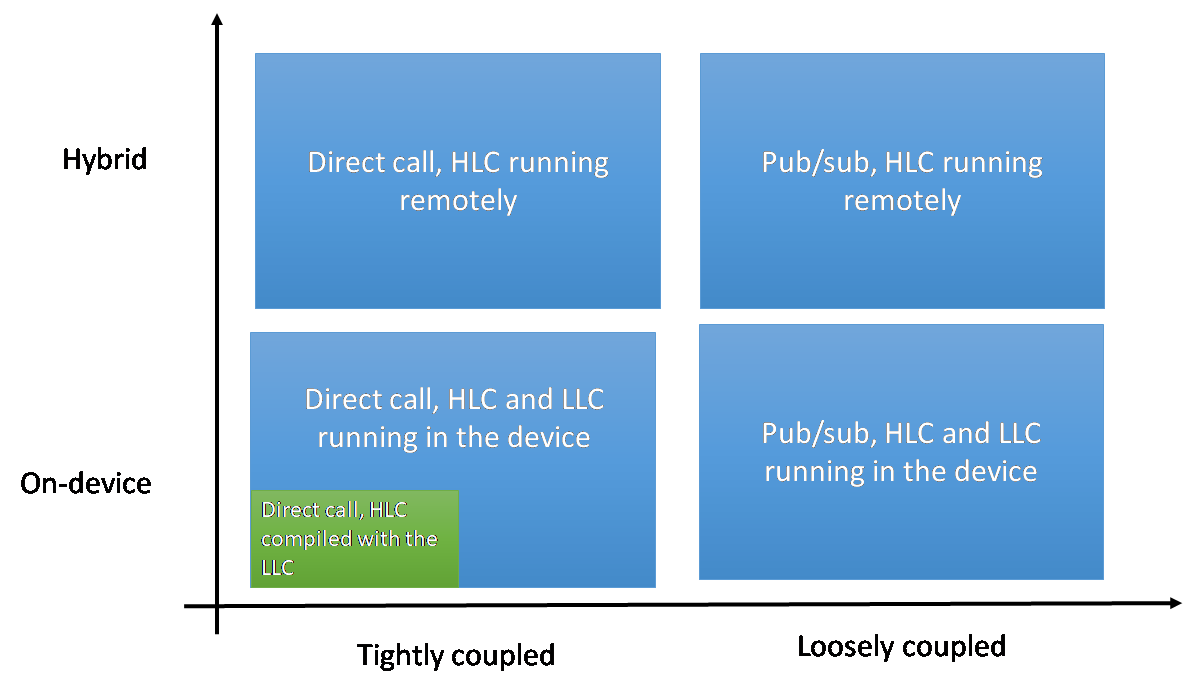
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 1: Categorisation and mapping of interface preacticies [3].
Outlook and Next Steps
At the moment, the IEEE P2660.1 WG is defining the method to select the recommended interface practice for a given application scenario, considering a collection of best interfacing practices, technologically instantiated from the identified group of templates, and their characteristics for a set of criteria that includes response time, scalability, robustness and re-usability. The establishment of these recommendation practices may contribute to mitigate the current lacks and boost the adoption of MAS and CPS-based approaches by industry.
References
- P. Leitão, Agent-based Distributed Manufacturing Control: A State-of-the-art Survey, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 22, n. 7, pp. 979-991, 2009.
- P. Leitão, S. Karnouskos, L. Ribeiro, P. Moutis, J. Barbosa, T. Strasser, “Common Practices for Integrating Industrial Agents and Low Level Automation Functions”, Proceedings of the 43th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON'17), 2017, pp. 6665-6670 (DOI: 10.1109/IECON.2017.8217164).
- P. Leitão, S. Karnouskos, L. Ribeiro, P. Moutis, J. Barbosa, T. Strasser, “Integration Patterns for Interfacing Software Agents with Industrial Automation Systems”, Proceedings of the 44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON’18), 2018, pp. 2908-2913 (DOI: 10.1109/IECON.2018.8591641)
Contributers
 |
Paulo Leitao, IEEE Senior Member, is Professor at the Polytechnic Institute of Bragança, Portugal, and Coordinator of the Research Centre in Digitalization and Intelligent Robotics (CeDRI). His research interests are in the field of intelligent and reconfigurable systems, cyber-physical systems, Internet of Things, multi-agent systems and distributed data analysis. He participates in several national and international R&D projects, served as general chair of several international conferences, published 4 books and more than 200 papers in international scientific journals and conference proceedings. He is chairing the IEEE Standards Association P2660.1 Working Group and is the past Chair of the IEEE IES Technical Committee on Industrial Agents. |
 |
Thomas Strasser, IEEE Senior Member, is a Senior Scientist with the Center for Energy at the AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, Vienna, Austria. His main responsibilities involve the strategic development of smart grid automation and validation research projects where he also leads the European-funded research infrastructure project ERIGrid. Besides that, he is active as a Senior Lecturer (Privatdozent) with the Vienna University of Technology. |
9 July 2019
Past Issues
To view archived articles, and issues, which deliver rich insight into the forces shaping the future of the smart cities. Older eNewsletter can be found here. To download full issues, visit the publications section of the IEEE Smart Cities Resource Center.



